
Microfinance has emerged as a potent instrument for fostering financial inclusion and expanding credit accessibility in India, particularly for low-income individuals and marginalized communities who lack access to conventional banking services. Among the most noteworthy aspects of microfinance in India are micro loans, which are modest-sized loans extended to disadvantaged individuals to bolster their livelihoods and small-scale business ventures. In this exploration, we will delve into what micro lending entails, explore the various types available, elucidate their advantages, and elucidate the application process for these loans in India.
Understanding Microfinance Loans
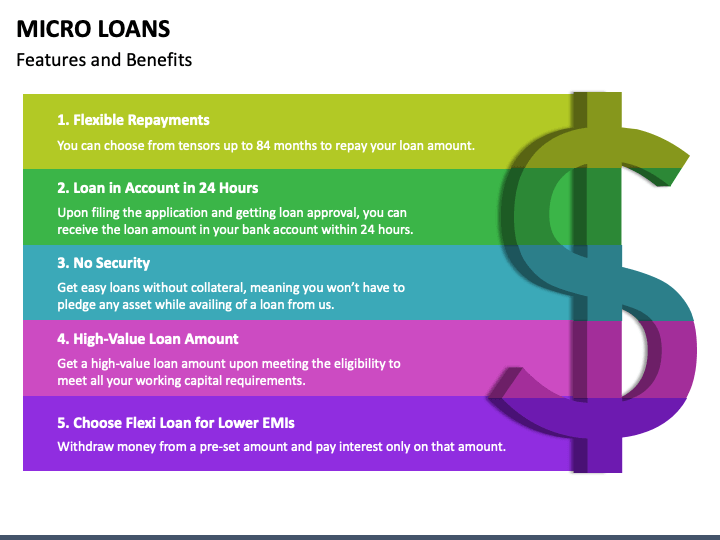
Micro Loans, as their name implies, are small-scale credit offerings designed for small business proprietors in India. These loans are extended to entrepreneurs who otherwise would not have access to traditional credit facilities due to limited income or lack of collateral. The primary objective is to equip them with essential resources in the form of micro business loans, enabling them to initiate new enterprises, secure their livelihoods, and augment their savings. Typically, these loans are of relatively modest amounts, and the terms for repayment are structured to be flexible and manageable for borrowers.
Diverse Categories of Microfinance
Microfinance facilities in India encompass a range of categories:
- Micro Loans: These are the fundamental type of microfinance loans, typically offered to individuals or small-scale entrepreneurs who lack access to traditional banking services due to their low income or absence of collateral. The loan amounts are relatively small and can be used for various purposes, including launching or expanding small businesses, acquiring livestock, financing agricultural activities, or addressing urgent financial needs. Micro loans often feature lower interest rates and more extended repayment periods than traditional bank loans, and they can be easily applied for online.
- Micro Savings: Microfinance institutions actively promote and facilitate micro savings among their clients. These savings products are designed to help individuals create a financial safety net and cultivate a habit of regular saving. Micro savings accounts typically have minimal to zero opening balance requirements and accrue interest to incentivize increased savings. This financial discipline not only aids individuals in managing their expenses but also makes them eligible for larger loans in the future.
- Micro Insurance: Micro insurance constitutes another crucial facet of microfinance in India. It provides insurance coverage tailored to the specific needs of low-income individuals, safeguarding them against various risks such as health emergencies, crop failures, accidents, and natural disasters. Micro insurance ensures that the economically disadvantaged do not slip further into poverty when confronted with unforeseen circumstances.
Advantages of Microfinance
Micro lending yields several benefits that contribute to the economic development of underserved communities. These include:
- Financial Inclusion: Microfinance extends financial services to those who struggle to access credit through formal banking channels, significantly bolstering financial inclusion and economic participation.
- Poverty Alleviation: By providing capital for income-generating activities, microfinance contributes to poverty reduction and the advancement of small businesses.
- Women Empowerment: Microfinance has played a pivotal role in empowering women by affording them financial independence and decision-making authority within households and businesses.
- Promotion of Entrepreneurship: Micro loans stimulate the growth of small businesses and entrepreneurship, fostering economic expansion and job creation at the grassroots level.
- Social Development: Microfinance plays a vital role in addressing social issues such as education, healthcare, and sanitation by enabling individuals to afford essential services.
The Mechanisms of Microfinance in India
Micro lending in India operates through two primary modes:
- SHG Bank Linkage Programme for Microfinance: One of the most successful microfinance models in India is the Self-Help Group (SHG) Bank Linkage Programme. Under this scheme, women from similar socioeconomic backgrounds form self-help groups. These groups pool their savings, which are then connected to mainstream banks. The banks extend loans to the SHGs, and the groups subsequently lend the funds to their members based on their requirements. This program has proven highly effective in reaching rural impoverished populations and empowering women.
- Microfinance Institutions: In addition to the SHG Bank Linkage Programme, various Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) in India provide microfinance services. MFIs are specialized financial entities offering an array of microfinance products, including micro business loans, micro savings, and micro insurance. They cater to both rural and urban demographics, with a mission to alleviate poverty and advance financial inclusion.
How to Apply for Microfinance Loans in India
The process for applying for microfinance loans in India generally encompasses the following steps:
- Research: Identify the MFI or SHG operating in your vicinity and research the types of loans they offer, their eligibility criteria, interest rates, and repayment terms.
- Documentation: Assemble the requisite documents, including identity proof, address proof, income details, and any other documents stipulated by the microfinance institution.
- Application: Complete the loan application form provided by the institution and submit it along with the necessary documentation.
- Credit Assessment: The institution will conduct a credit assessment to evaluate your capacity to repay and your creditworthiness.
- Loan Disbursement: If your loan application is approved, the funds will be disbursed to you in accordance with the agreed-upon terms.
- Repayment: Make regular repayments as per the terms agreed with the institution to maintain a favorable credit history and qualify for future loans.
In Conclusion
Microfinance facilities, including micro loans, savings, and insurance, have emerged as a lifeline for disadvantaged individuals in India, enabling them to enhance their lives, establish sustainable businesses, and contribute to the nation’s economic advancement. Through various micro lending models such as the SHG Bank Linkage Programme and Microfinance Institutions, millions of people have gained access to financial services and opportunities for socio-economic development.
As the financial landscape evolves, institutions like LICHFL actively work to expand credit access. This includes offering different financing options such as business loans and personal loans to meet diverse financial needs. As microfinance continues to evolve and expand, it will play an increasingly significant role in addressing poverty and advancing financial inclusion in India.



Leave a Reply